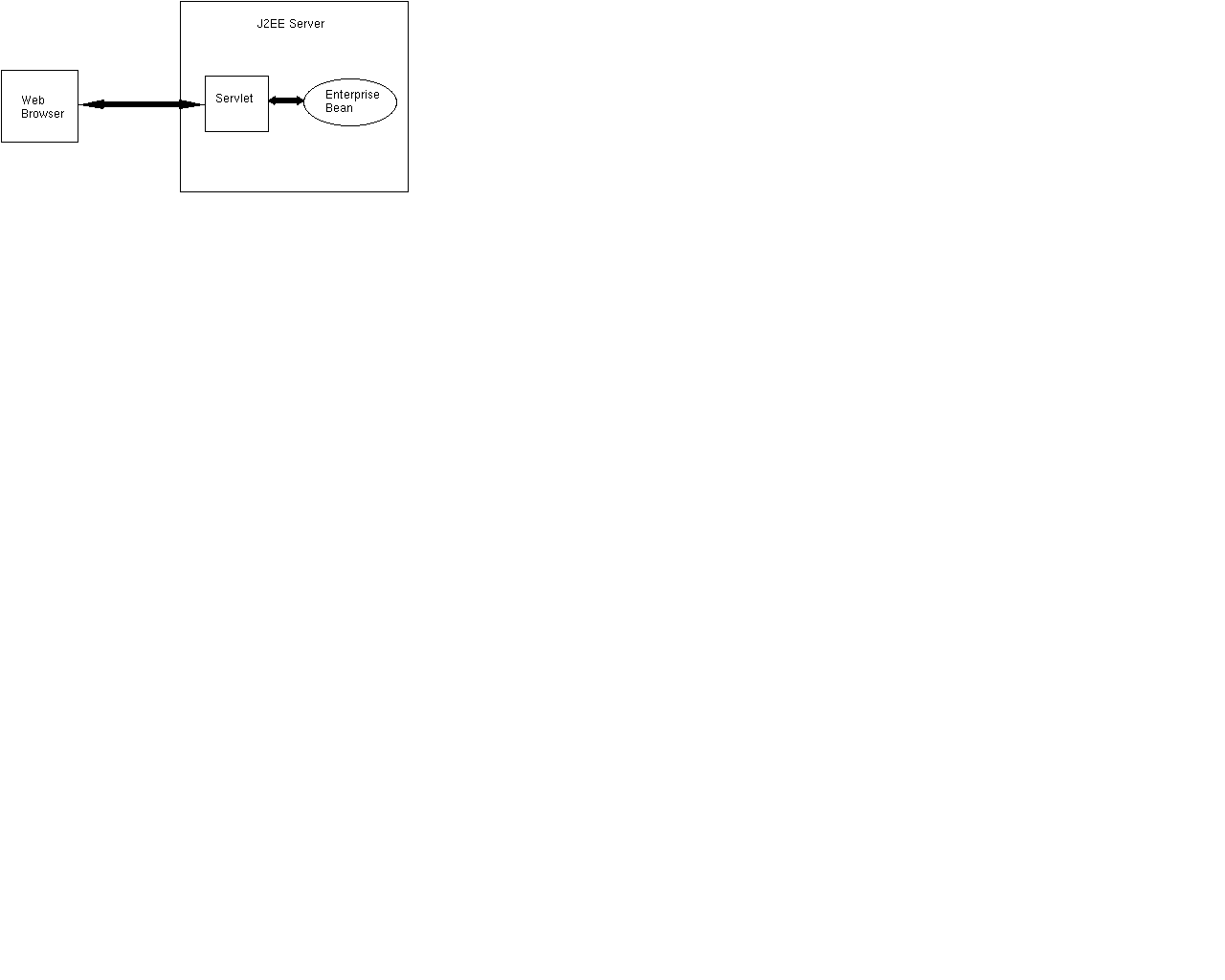
This document provides basic instructions for deploying and running Sun's J2EE Developer's Guide, version 1.2.1 EJB samples on iPlanet Application Server. Each sample is very simple and emphasizes a specific aspect of EJBs. iPlanet has augmented the original Sun samples with instructions for deploying the samples to iPlanet Application Server. Before deploying the following samples:
To deploy the J2EE Developer's Guide samples to iPlanet, refer to the "iPlanet Setup Instructions" column in the following table. The "Sun Tutorial Documentation" column provides links to the original Sun documentation describing the J2EE-based programming practices associated with each application.
| Topic Demonstrated
by the Example |
iPlanet Setup Instructions | Sun Tutorial Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| simple stateless session bean | converter | "Getting Started" |
| stateful session bean w. exception and helper class |
cart | "A Session Bean Example" |
| environment entry | checker | "Accessing Environment Entries" |
| entity bean w. bean-managed persistence |
account | "A Bean-Managed Persistence Example" |
| entity bean w. container-managed persistence |
product | "A Container-Managed Persistence Example" |
| entity beans w. one:one relationships |
storagebin | "One-to-One Relationships" |
| entity beans w. one:many relationships and helper classes |
order | "A Helper Class for the Child Table" |
| entity beans (2) w. one:many relationships |
salesrep | "An Entity Bean for the Child Table" |
| entity beans w. many:many relationships |
enroller | "Many-to-Many Relationships" |
| database connection | account | "How to Connect" |
| container-managed transaction |
bank | "Container-Managed Transactions" |
| bean-managed, JDBCTM transaction |
warehouse | "JDBC Transactions" |
| bean-managed, JTA transaction |
teller | "JTA Transactions" |
| stand-alone JavaTM
application client |
converter | "Stand-Alone JavaTM Applications" |
| J2EE application client | "J2EE Application Clients" | |
| servlet client of an enterprise bean |
adder | "Servlets" |
| JSP client w. JavaBeansTM comp. |
jsptobean | "JavaServer PagesTM Components" |
| enterprise bean client | shipper | "Other Enterprise Beans" |
| JSP client w. tag extension |
jsptag | "Accessing Enterprise Beans Through JSP Tag Libraries" |
| enterprise bean sending an email |
confirmer | "Sending Email from an Enterprise Bean" |
| enterprise bean connecting to a URL |
urlconnect | "Connecting to a URL in an Enterprise Bean" |
AccountEJB.java was modified to move the logic for obtaining a connection from setEntityContext() to the private helper methods that need to interact with the database. Since the application server supports connections pooling, it is much more efficient to obtain a connection from the pool per EJB method invocation than to have potentially many copies of EJBs holding connections from the pool for an extended period of time.
A servlet named AccountServlet.java has been added to provide a web-based means of exercising the Account EJB.
Setup Database Table
Using PointBase
If Pointbase is the target database, then nothing needs to be done since the database is prepopulated. However, if you do want to navigate the database tables or want to unload and create the tables from scratch (using the account_pb.sql script in the src/schema directory), follow the instructions in the Using Pointbase with iPlanet guide.
However, the datasource needs to be registered. To do this,
Go to the directory
install_dir/ias/ias-samples/j2eeguide/account/src/schema.
Execute the command
iasdeploy regdatasource AccountDB-pointbase-type4.xml
After registering the datasource, go to the next section to assemble the application.
Using Oracle
The Account sample's database setup script will register the jdbc/j2eeguide/AccountDB datasource in the application server and then create a simple table named ACCOUNT in the database. Since the Account sample adds rows to the database, no rows are added by the database setup script.
setup_ora.sh <TNS Name> <user name> <user password>
For example,
setup_ora.sh orcl j2eeguide j2eeguide
Compile EJB Sources
Create j2eeguide-accountEjb.jar ModuleTo compile the application sources, simply execute "build compile" under the application's src/ directory. See the Sample Application Build Facility document for more information on using a build facility to quickly compile the application.
See Assemble EJB JAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Create j2eeguide-account.war Module
This is an optional step. If you plan on using the AccountServlet to access the Account EJB, then follow these instructions. If you plan to use the AccountClient with RMI/IIOP as the only method of accessing the Account EJB, then skip to the next series of steps to create the EAR file.
See Assemble WAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Assemble j2eeguide-account.ear
See Assemble EAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Deploy the Server Application
See EJB deployment steps in Converter documentation.
Deploy the Client ApplicationSee client deployment steps in Converter documentation. Steps for the Account sample are identical to those for Converter except for the following considerations:
See Running the Application in Converter documentation. Review the troubleshooting information as well. For Account, you should expect the following output on the client side:
root@ias-{$PWD}: java j2eeguide.account.AccountClient localhost 9010Compare this output with the AccountClient.java source code.
balance = 68.25
balance = 32.55
456: 44.77
730: 19.54
268: 100.07
456: 44.77
836: 32.55
After client application completes, the database should have the following information:
SSQL> select * from account;ID FIRSTNAME LASTNAME BALANCE
--- ------------------------ ------------------------ ----------
456 Pat Smith 44.77
836 Joe Jones 32.55
730 John Smith 19.54
268 Mary Smith 100.07
Run the Servlet Client
Go to the following URL to exercise the servlet front end:
http://<hostname>/NASApp/j2eeguide-account/AccountServlet
If your deployment process was successful, the servlet sends the same information to the browser as seen when running the RMI/IIOP client.
Troubleshooting Whenever the client application does not display the output listed above,
you should go into the database and manually clean the Account table.
If you see the following message in the kjs log file, it is most likely caused
by an attempt to perform an EJB create of the Account bean with the same primary
key as previous create attempt. To fix this problem, either go into
the database and delete the existing rows from the account table or rerun the
setup_ora script to drop and create the table again.
[25/Apr/2000 09:31:50:0] warning: ORCL-002: GXORCL2PreparedStatement::DAEExecute(): ORA-00001: unique constraint (IASDEMO.PK_ACCOUNT) violated
In this case, the client sees a java.lang.NullPointerException.
If you are using PointBase, you can remove and recreate the sample table by using the supplied src/schema/account_pb.sql script and the PointBase tools described in Using PointBase with iPlanet guide.
As part of your troubleshooting efforts, ensure that you review the General Troubleshooting section to learn how to view logs files. Also review the Troubleshooting section of the RMI/IIOP chapter of the Developer's Guide.
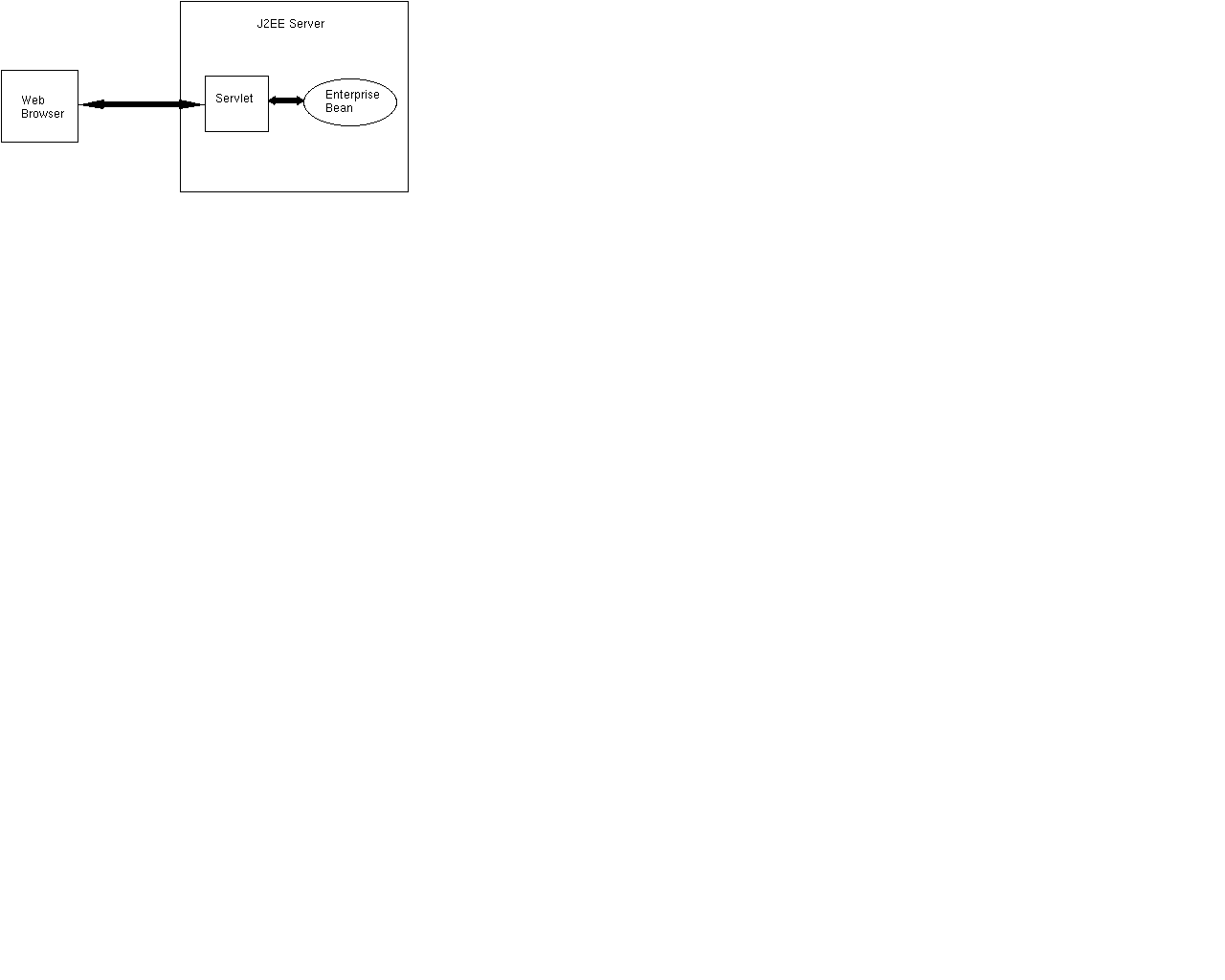
In the AdderServlet, the reference to the Adder EJB is saved in a instance variable of the servlet rather than in HttpSession. This artifact of the sample from Sun means that multiple users of the same servlet instance will access the same stateful session bean instance. In a production application, a more appropriate approach would be to save the Handle to the EJB instance in the HttpSession instance associated with each web session.
Create j2eeguide-adderEjb.jar ModuleTo compile the application sources, simply execute "build compile" under the application's src/ directory. See the Sample Application Build Facility document for more information on using a build facility to quickly compile the application.
See Assemble EJB JAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Create j2eeguide-adder.war Module
See Assemble WAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
See Assemble EAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
See the deployment steps in Converter documentation.
Run the ApplicationGo to the following URL to exercise the servlet front end:
http://<hostname>/NASApp/j2eeguide-adder/adder.html
Enter a number and press submit. The AdderServlet will interact with the Adder EJB to add the value to a running total and display the resulting total in a web page. Enter another number and press submit again to see the updated total. Negative numbers will work as well.
TroubleshootingAs part of your troubleshooting efforts, ensure that you review the General
Troubleshooting section to learn how to view logs files.
Setup Database Table
Using PointBase
If Pointbase is the target database, then nothing needs to be done since the database is prepopulated. However, if you do want to navigate the database tables or want to unload and create the tables from scratch (using the bank_pb.sql script in the src/schema directory), follow the instructions in the Using Pointbase with iPlanet guide.
However, the datasource needs to be registered. To do this,
Go to the directory
install_dir/ias/ias-samples/j2eeguide/bank/src/schema.
Execute the command
iasdeploy regdatasource BankDB-pointbase-type4.xml
After registering the datasource, go to the next section to assemble the application.
Using Oracle
The Bank sample's database setup script will register the jdbc/j2eeguide/BankDB datasource with the application server and then create a simple table named BANK in the database.
setup_ora.sh <TNS Name> <user name> <user password>
For example,
setup_ora.sh orcl j2eeguide j2eeguide
Compile EJB and servlet sources
Create j2eeguide-bankEjb.jar Module
See Assemble EJB JAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Create j2eeguide-bank.war Module
This is an optional step. If you plan on using the BankServlet to access the Bank EJB, then follow these instructions. If you plan to use the BankClient RMI/IIOP method of accessing the Bank EJB, then skip to the next series of steps to create the EAR file.
See Assemble WAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Assemble j2eeguide-bank.ear
See Assemble EAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Deploy the Server Application
See EJB deployment steps in Converter documentation.
Deploy the Client ApplicationSee client deployment steps in Converter documentation. Steps for the Bank sample are identical to those for Converter except for the following considerations:
You have the option of using either the web client or the RMI/IIOP Java application client to exercise the Bank sample. Regardless of the client, before running the application, review the initial state of the CHECKING and SAVING database tables.
SQL> select * from saving;
ID BALANCE
--- ---------
123 500SQL> select * from checking;
ID BALANCE
--- ---------
123 100
Run the Servlet Client
Go to the following URL to exercise the servlet front end:
http://<hostname>/NASApp/j2eeguide-bank/BankServlet
If your deployment process was successful, the following information will be displayed:
checking: 20.0
saving: 580.0Compare this output with the BankClient.java source code.
In the kjs log file, you should see the following output. BankServlet generates the output represented in bold:
Reload the URL in the browser and you will see the following:[25/Jul/2000 11:22:46:1] info: --------------------------------------
[25/Jul/2000 11:22:46:1] info: BankServlet: init
[25/Jul/2000 11:22:46:1] info: --------------------------------------
looking up java:comp/env/MyBank
lookup ok
Lookup instance 5028cf0
afterBegin()
beforeCompletion()
afterCompletion: true
Unregister Object 5028cf0checking: 20.0Note that since there are only 20 dollars remaining in the checking account and each execution of the BankServlet attempts to transfer 40 dollars from checking to savings, another execution of the servlet should result in an exception. Reload the URL once more to see the following results:
saving: 580.0Caught an exception:unchecked exception thrown by impl j2eeguide.bank.BankEJB@81d2e; nested exception is: j2eeguide.bank.InsufficientBalanceExceptionSince the Bank EJB calls the context.setRollbackOnly() method after updating the CHECKING table and before throwing the InsufficientBalanceException, the container will automatically rollback the update to the CHECKING table prior to returning the InsufficientBalanceException to the client. Verify the rollback occurred by checking the database content again. You should observe the following after the rollback:SQL> select * from saving;If the rollback was not successful, you will see a negative balance in the CHECKING table.ID BALANCE
--- ---------
123 580SQL> select * from checking;
ID BALANCE
--- ---------
123 20To rerun the application from scratch, reload the database tables and follow the run steps again.
If you are using PointBase, you can remove and recreate the sample table by using the supplied src/schema/bank_pb.sql script and the PointBase tools described in Using PointBase with iPlanet guide.
Run the RMI/IIOP Client
See Running the Application in Converter documentation. Review the troubleshooting infomation as well. For Bank, you should expect the following output on the client side:
root@ias-{$PWD}: java j2eeguide.bank.BankClient localhost 9010
checking: 20.0
saving: 580.0
Troubleshooting
As part of your troubleshooting efforts, ensure that you review the General Troubleshooting section to learn how to view logs files. Also review the Troubleshooting section of the RMI/IIOP chapter of the Developer's Guide.
A servlet named CartServlet.java has been added to provide a web-based means of exercising the Cart EJB.
Assemble and Deploy Cart Application
Compile EJB Sources
To compile the application sources, simply execute "build compile" under the application's src/ directory. See the Sample Application Build Facility document for more information on using a build facility to quickly compile the application.
Create j2eeguide-cartEjb.jar Module
See Assemble EJB JAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Create j2eeguide-cart.war Module
This is an optional step. If you plan on using the CartServlet to access the Cart EJB, then follow these instructions. If you plan to use the CartClient RMI/IIOP method of accessing the Cart EJB, then skip to the next series of steps to create the EAR file.
Assemble j2eeguide-cart.ear
See Assemble EAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Deploy the Server Application
See EJB deployment steps in Converter documentation.
Deploy the Client ApplicationSee client deployment steps in Converter documentation. Steps for the Cart sample are identical to those for Converter except for the following considerations:
See Running the Application in Converter documentation. Review the troubleshooting infomation as well. You should expect the following output on the client side:
root@ias-{$PWD}: java j2eeguide.cart.CartClient localhost 9010Compare this output with the CartClient.java source code.
looking up java:comp/env/MyCart lookup ok
The Martian Chronicles
2001 A Space Odyssey
The Left Hand of Darkness
Caught a BookException: Alice in Wonderland not in cart.
Run the Servlet Client
Go to the following URL to exercise the servlet front end:
http://<hostname>/NASApp/j2eeguide-cart/CartServlet
If your deployment process was successful, the servlet sends the same information to the browser as seen when running the RMI/IIOP client.
TroubleshootingAs part of your troubleshooting efforts, ensure that you review the General Troubleshooting section to learn how to view logs files. Also review the Troubleshooting section of the RMI/IIOP chapter of the Developer's Guide.
Compile EJB Sources
Create j2eeguide-checkerEjb.jar ModuleTo compile the application sources, simply execute "build compile" under the application's src/ directory. See the Sample Application Build Facility document for more information on using a build facility to quickly compile the application.
See Assemble EJB JAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Create j2eeguide-checker.war Module
This is an optional step. If you plan on using the CheckerServlet to access the Checker EJB, then follow these instructions. If you plan to use the CheckerClient RMI/IIOP method of accessing the Checker EJB, then skip to the next series of steps to create the EAR file.
See Assemble WAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Assemble j2eeguide-checker.ear
See Assemble EAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Deploy the Server Application
See EJB deployment steps in Converter documentation.
Deploy the Client Application
See client deployment steps in Converter documentation. Steps for the Checker sample are identical to those for Converter except for the following considerations:
See Running the Application in Converter documentation. Review the troubleshooting infomation as well. For Checker, you should expect the following output on the client side:
root@ias-{$PWD}: java j2eeguide.checker.CheckerClient localhost 9010Compare this output with the CheckerClient.java source code.
discount = 4800.0
Run the Servlet Client
Go to the following URL to exercise the servlet front end:
http://<hostname>/NASApp/j2eeguide-checker/CheckerServlet
If your deployment process was successful, the servlet sends the same information to the browser as seen when running the RMI/IIOP client.
TroubleshootingAs part of your troubleshooting efforts, ensure that you review the General Troubleshooting section to learn how to view logs files. Also review the Troubleshooting section of the RMI/IIOP chapter of the Developer's Guide.
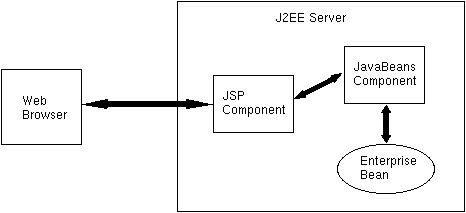
Since the j2eeguide-accountEjb.jar file will be included in the j2eeguide-jsptobean.ear file, you must ensure that this EJB JAR file exists and has been tested. If you already ran the Account sample, then this EJB JAR file should be available under the following directory:
ias-samples/j2eeguide/account/assemble/If you have not already ran the Account sample, then you need to do so at this stage. See the Account setup instructions. (Hint: to recreate the j2eeguide-accountEjb.jar file, you can simply go to the Account src/ directory and execute the "build" command).
Setup Database Table
Refer to the earlier Account sample if you have not
already setup the database table for the Account entity bean.
Assemble and Deploy Application
ias-samples/j2eeguide/account/src/
ias-samples/j2eeguide/jsptobean/src/
Create j2eeguide-jsptobean.war Module
See Assemble WAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
See Assemble EAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Deploy the Server Application
See EJB deployment steps in Converter documentation.
Run the ApplicationGo to the following URL to exercise the servlet front end:
http://<hostname>/NASApp/j2eeguide-jsptobean/Account.jsp
To create a new account, follow these steps:
1. In the AccountID field, enter a three-digit integer.
2. In the Balance field, enter the initial balance (for example, 100.00).
3. In the First Name and Last Name fields enter your name.
4. Under Action, select Create.
5. Click the Submit button.
To credit an account, perform the following tasks:
1. In the AccoundID field, enter the three-digit account identifier.
2. In the Amount field, enter the credit amount (for example, 55.00).
3. Under Action, select Credit.
4. Click the Submit button.
Review the content of the Account database table directly by using sqlplus
or an equivalent tool.
Troubleshooting
As part of your troubleshooting efforts, ensure that you review the General Troubleshooting section to learn how to view logs files. Also review the Troubleshooting section of the RMI/IIOP chapter of the Developer's Guide.
Compile EJB Sources
To compile the application sources, simply execute "build compile" under the application's src/ directory. See the Sample Application Build Facility document for more information on using a build facility to quickly compile the application.
Create j2eeguide-warehouseEjb.jar Module
See Assemble EJB JAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
This is an optional step. If you plan on using the WarehouseServlet to access the Warehouse EJB, then follow these instructions. If you plan to use the WarehouseClient RMI/IIOP method of accessing the Warehouse EJB, then skip to the next series of steps to create the EAR file.
See Assemble WAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
See Assemble EAR steps in Converter documentation for additional details.
Deploy the Server Application
See EJB deployment steps in Converter documentation.
Deploy the Client Application
See client deployment steps in Converter documentation. Steps for the Warehouse sample are identical to those for Converter except for the following considerations:
You have the option of using either the web client or the RMI/IIOP Java application client to exercise the Warehouse sample. Regardless of the client, before running the application, review the initial state of the INVENTORY and ORDER_ITEM database tables.
Run the Web ClientSQL> select * from order_item;ORD PRO STATUS
--- --- --------
456 123 openSQL> select * from inventory;
PRO QUANTITY
--- ---------
123 100
Go to the following URL to exercise the application:Run the RMI/IIOP Clienthttp://<hostname>/NASApp/j2eeguide-warehouse/WarehouseServletCompare the following output with the WarehouseServlet.java source code. You should see the following web content displayed in the browser:looking up java:comp/env/MyWarehouseSince the sample client ships a quantity of 8 items of product_id 123, the tables should look like the following after running the sample:
lookup ok
create successful
status = shippedSQL> select * from order_item;You can run the sample repeatedly to see the QUANTITY decrease by 8 after each execution.ORD PRO STATUS
--- --- --------
456 123 shippedSQL> select * from inventory;
PRO QUANTITY
--- ---------
123 92To force an exception to occur in the middle of the JDBC transaction, follow these steps:
- If you are using Oracle, execute schema/setup_ora.bat/.sh again to reset the database tables for this example. If you are using PointBase, you can remove and recreate the sample table by using the supplied src/schema/warehouse_pb.sql script and the PointBase tools described in Using PointBase with iPlanet guide.
- drop the INVENTORY table.
- run the sample again.
- check the kjs log to see the transaction failure exception:
[01/Aug/2000 18:16:27:1] info: --------------------------------------
[01/Aug/2000 18:16:27:1] info: WarehouseServlet: init
[01/Aug/2000 18:16:27:1] info: --------------------------------------
[01/Aug/2000 18:16:31:0] warning: ORCL-002: PrepareQuery oparse(): ORA-00942: table or view does not exist[01/Aug/2000 18:16:31:2] warning: EB-invalidate_delegate: instance j2eeguide.warhouse.WarehouseEJB@62937c threw an unchecked or system exception, ex = javax.ej.EJBException: Transaction failed: prepStmt(): unable to prepare an internal statement object
[01/Aug/2000 18:16:31:2] error: Exception Stack Trace:
javax.ejb.EJBException: Transaction failed: prepStmt(): unable to prepare an internal statement object
at j2eeguide.warehouse.WarehouseEJB.ship(WarehouseEJB.java:34)
at j2eeguide.warehouse.ejb_skel_j2eeguide_warehouse_WarehouseEJB.ship(ejb_skel_j2eeguide_warehouse_WarehouseEJB.java:101)
at j2eeguide.warehouse.ejb_kcp_skel_Warehouse.ship__void__indir_wstring__indir_wstring__int(ejb_kcp_skel_Warehouse.java:269)
at com.kivasoft.ebfp.FPRequest.invokenative(Native Method)
at com.kivasoft.ebfp.FPRequest.invoke(Unknown Source)
at j2eeguide.warehouse.ejb_kcp_stub_Warehouse.ship(ejb_kcp_stub_Warehouse.java:399)
at j2eeguide.warehouse.ejb_stub_Warehouse.ship(ejb_stub_Warehouse.java:75)- Now check the ORDER_ITEM table to ensure that the STATUS still reflects "open".
SQL> select * from order_item;ORD PRO STATUS
--- --- --------
456 123 open
See Running the Application in Converter documentation. For Warehouse, you should expect the following output on the client side:root@ias-{$PWD}: java j2eeguide.warehouse.WarehouseClient localhost 9010The output from the WarehouseClient application should be almost identical to the output seen when running the WarehouseServlet client.Follow the steps in running the web client to verify that the application is running correctly. Then force an exception to occur during the transaction.
Troubleshooting
As part of your troubleshooting efforts, ensure that you review the General Troubleshooting section to learn how to view logs files. Also review the Troubleshooting section of the RMI/IIOP chapter of the Developer's Guide.
For the remaining EJB examples, review the Sun sample descriptions and examine the complete XML deployment descriptors and build.xml files to develop an understanding as to how to deploy the samples to iPlanet. As long as you've tried the Converter sample and perhaps several of the samples above, you should be able to determine how to deploy and exercise the following samples:
The basic steps for deploying each of these applications is to:
iPlanet is in the process of packaging the following sample for iPlanet and will publish them on developer.iplanet.com shortly: